A Closer Look at Infertility
- July 22,2020
- 5 Min Read

Infertility is a disorder of the reproductive system defined by the failure to achieve a clinical pregnancy after 12 months or more of regular unprotected sexual intercourse.
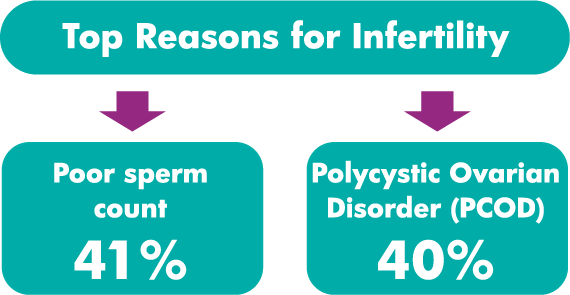 Nearly 30 million couples in India suffer from infertility.
Nearly 30 million couples in India suffer from infertility.
Top causes of Infertility in men:
- A history of having mumps
- Testicular injury
- Exposure to chemicals or toxins
- Acute illness or prolonged fever
- Drugs (marijuana, opiods, cimetidine, corticosteroids, methotrexate, antineoplastics drugs) or alcohol use
- Use of anabolic steroids
- Undescended testis
- Hormonal imbalance
- Klinefelter Syndrome
- Blocked fallopian tubes due to sexually transmitted diseases
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), which can interfere with ova release
- Uterine fibroids
- Endometriosis
- Autoimmune disorders, which produce antibodies against fetal tissues
- Diabetes
- Hypothyroidism
- Fluctuating or diminished hormone levels
- Eating disorders
- Obesity – increased Body Mass Index (BMI) has been associated with infertility and morbidity during pregnancy
- Gluten intolerance (celiac disease)
- Stress
- Multiple Partners
- Toxicity of Food
- Drug use
- Excessive Alcohol Drinking
- Smoking or Delayed Marriage
WHAT ARE INFERTILITY TESTS?
Infertility tests are done to help find out why a woman cannot become pregnant. The tests help find whether the problem is with the man, the woman, or both. Tests usually include a physical exam, semen analysis, blood tests, and special procedures.
Fertility tests for women
- Pelvic Ultrasound to discover abnormalities with the uterus, fallopian tubes and/or ovaries. Sonography can show evidence of pelvic scarring
- PAP Smear Test
- Rubella Antibody Test
- Test for Chlamydia trachomatis
- Test for Chlamydia trachomatis
- Blood test includes day 3
- FHS, LH, Prolactin
- Progesterone
- Testosterone (Free and Total)
- Estradiol
- Anti-Mullerian Hormone
- Free T3, free T4, and TSH
- DHEA-S
- Hysterosalpingogram (HSG) that evaluates the condition of the uterus and fallopian tubes.
- Further specialized tests like:
- TORCH 8
- TB Culture
- GeneXpert TB test
- Genetic testing (Chromosomal Karyotype)
- Procedures such as endometrial biopsy, laparoscopy and hysteroscopy
- Semen analysis to check for abnormalities in the number of sperms (concentration), motility (movement) and morphology (shape)
- Test for Chlamydia trachomatis which, in addition to being a known cause of infertility in women, can also affect sperm function
- Blood Tests include:
- Follicle stimulating Hormone (FHS)
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
- Prolactin
- Testosterone (Free and Total)
- Estradiol and SHBG
- Transrectal and Scrotal Ultrasound is done to look for evidence of conditions such as retrograde ejaculation and ejaculatory duct obstruction
Increase your chances of getting pregnant by:
- Avoid extreme weight loss or gain
- Exercise moderately
- Quit Smoking
- Limit Caffeine
- Limit alcohol
Tips to maintain healthy sperm count:
- Quit smoking
- Limit alcohol
- Exercise regularly
- Avoid high temperatures and exposure to industrial or environmental toxins
Most Viewed
Premarital Health Screening
- 20 Min Read
Typhoid - Signs and Symptoms
- 3 Min Read
Home Isolation Guidelines - Covid-19 Care
- 5 Min Read