Radiology Service
Digital X-Ray
At Suburban Diagnostics, we offer digital X-ray facilities that are environment friendly and accredited by the Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB). Digital X-rays are safer as compared to traditional X-rays as they reduce the amount of radiation that the patient is exposed to and also makes it simpler & easier to transfer, share and enhance images. They can be used for all routine X-rays as well as in specialized imaging studies like IVP (Intravenous Pyelogram).
X-rays done at Suburban Diagnostics:

Abdomen
Chest
Adenoids

Extremities
Joints

Kidney
PNS
Spine AP/Lateral
Sonography
Suburban Diagnostics offers a complete range of ultrasonographic procedures like:
- OBSTETRIC USG
- ROUTINE SONOGRAPHY
- NON-OBSTETRIC USG
- MUSCULOSKELETAL USG
All sonography procedures at Suburban Diagnostics are strictly in compliance with PCPNDT laws and we strongly discourage and oppose the practice of sex determination of the foetus.
Obstetric Sonography
This procedure is generally used to understand and examine the following in pregnancy:
- Routine obstetrics (growth scan, early pregnancy, assessment of cervical length, placental position)
- Nuchal scan/NT scan/early anomaly scan
- Second-trimester anomaly scan/targetted scan/malformation scan
- Fetal echocardiography
- Obstetric doppler
- Biophysical profile
Early pregnancy
USG is done in early pregnancy to confirm the pregnancy as well as its position (intrauterine or extra-uterine). A gestational sac can be reliably seen on transvaginal ultrasound by 5 weeks’ gestational age (approximately 3 weeks after ovulation).
First Trimester
In the first trimester, a standard ultrasound examination typically includes:
- Gestational sac size, location, and number
- Identification of the embryo and/or yolk sac
- Measurement of fetal length (known as the crown-rump length)
- Fetal number, including the number of amniotic sacs and chorionic sacs for multiple gestations
Second and Third Trimester
In the second and third trimester, a standard ultrasound examination typically includes:
- Evaluation of the maternal uterus, tubes, ovaries, and surrounding structures when appropriate
- Ultrasonography of the cervix
- Fetal number, including the number of amniotic sacs and chorionic sacs for multiple gestations
- Fetal cardiac activity
- Fetal position relative to the uterus and cervix
- Amniotic fluid volume
- Location and appearance of the placenta, including the site of umbilical cord insertion when possible
- Gestational age assessment
- Fetal weight estimation
- Fetal anatomical survey
Obstetric sonography has become useful in the assessment of the cervix in women at risk for premature birth. A short cervix preterm is undesirable. At 24 weeks’ gestation a cervix length of less than 25 mm defines a risk group for preterm birth, further, the shorter the cervix the greater the risk. It also has been helpful to use ultrasonography in women with preterm contractions, as those whose cervix length exceeds 30 mm are unlikely to deliver within the next week.
Non-Obstetric / Gynec Sonography
We perform ultrasound imaging which uses sound waves to produce pictures of :
- USG pelvis
- Follicular monitoring / ovulation studies
- AFC count
- Pelvis Doppler
Routine sonography
Routine sonography is suggested for the various organs as following:
- Whole abdomen / abdomen and pelvis
- Detailed ultrasound assessment of all abdominal organs including liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, bladder, prostate and intestines
- Upper abdomen
- Detailed ultrasound assessment of all abdominal organs including liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, bladder
- Detailed ultrasound assessment with specific focus on organs of urinary system including kidneys, bladder, prostate (in males) and uterus/ovaries (in females) with assessment of prevoid capacity of bladder and postvoid residue
- Transrectal Ultrasonography (TRUS)
- Also known as Transrectal Ultrasonography of the prostate, this is a detailed evaluation of prostate through a transrectal approach. In this procedure an ultrasonography probe is introduced per rectally for better understanding of the prostate sonomorphology and to rule out any suspicious lesions in the prostate
- Inguinal regions
- High resolution USG is done to rule out hernias or any other pathology in the inguinal regions
- Scrotum
- Detailed ultrasound assessment of the testis
- Neck / Thyroid
- Detailed ultrasound assessment of the thyroid gland, submandibular, parotid glands as well as to confirm/rule out the presence of any enlarged cervical lymph nodes Sonomammography / USG Breast
- USG Penis
- Small parts / Soft tissue Sonography
- Kidney, ureter and bladder (KUB)
- Sonomammography / USG Breast
- Kidney, ureter and bladder (KUB)
Obstetric Sonography
Obstetric Sonography
This procedure is generally used to understand and examine the following in pregnancy:
- Routine obstetrics (growth scan, early pregnancy, assessment of cervical length, placental position)
- Nuchal scan/NT scan/early anomaly scan
- Second-trimester anomaly scan/targetted scan/malformation scan
- Fetal echocardiography
- Obstetric doppler
- Biophysical profile
Early pregnancy
Early pregnancy
USG is done in early pregnancy to confirm the pregnancy as well as its position (intrauterine or extra-uterine). A gestational sac can be reliably seen on transvaginal ultrasound by 5 weeks’ gestational age (approximately 3 weeks after ovulation).
First Trimester
In the first trimester, a standard ultrasound examination typically includes:
- Gestational sac size, location, and number
- Identification of the embryo and/or yolk sac
- Measurement of fetal length (known as the crown-rump length)
- Fetal number, including the number of amniotic sacs and chorionic sacs for multiple gestations

Second and Third Trimester
Second and Third Trimester
In the second and third trimester, a standard ultrasound examination typically includes:
- Evaluation of the maternal uterus, tubes, ovaries, and surrounding structures when appropriate
- Ultrasonography of the cervix
- Fetal number, including the number of amniotic sacs and chorionic sacs for multiple gestations
- Fetal cardiac activity
- Fetal position relative to the uterus and cervix
- Amniotic fluid volume
- Location and appearance of the placenta, including the site of umbilical cord insertion when possible
- Gestational age assessment
- Fetal weight estimation
- Fetal anatomical survey
Obstetric sonography has become useful in the assessment of the cervix in women at risk for premature birth. A short cervix preterm is undesirable. At 24 weeks’ gestation a cervix length of less than 25 mm defines a risk group for preterm birth, further, the shorter the cervix the greater the risk. It also has been helpful to use ultrasonography in women with preterm contractions, as those whose cervix length exceeds 30 mm are unlikely to deliver within the next week.


Non-Obstetric / Gynec Sonography
Non-Obstetric / Gynec Sonography
We perform ultrasound imaging which uses sound waves to produce pictures of :
- USG pelvis
- Follicular monitoring / ovulation studies
- AFC count
- Pelvis Doppler
Routine sonography
Routine sonography
Routine sonography is suggested for the various organs as following:
- Whole abdomen / abdomen and pelvis
- Detailed ultrasound assessment of all abdominal organs including liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, bladder, prostate and intestines
- Upper abdomen
- Detailed ultrasound assessment of all abdominal organs including liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, bladder
- Detailed ultrasound assessment with specific focus on organs of urinary system including kidneys, bladder, prostate (in males) and uterus/ovaries (in females) with assessment of prevoid capacity of bladder and postvoid residue
- Transrectal Ultrasonography (TRUS)
- Also known as Transrectal Ultrasonography of the prostate, this is a detailed evaluation of prostate through a transrectal approach. In this procedure an ultrasonography probe is introduced per rectally for better understanding of the prostate sonomorphology and to rule out any suspicious lesions in the prostate
- Inguinal regions
- High resolution USG is done to rule out hernias or any other pathology in the inguinal regions
- Scrotum
- Detailed ultrasound assessment of the testis
- Neck / Thyroid
- Detailed ultrasound assessment of the thyroid gland, submandibular, parotid glands as well as to confirm/rule out the presence of any enlarged cervical lymph nodes Sonomammography / USG Breast
- USG Penis
- Small parts / Soft tissue Sonography
- Kidney, ureter and bladder (KUB)
- Sonomammography / USG Breast
- Kidney, ureter and bladder (KUB)
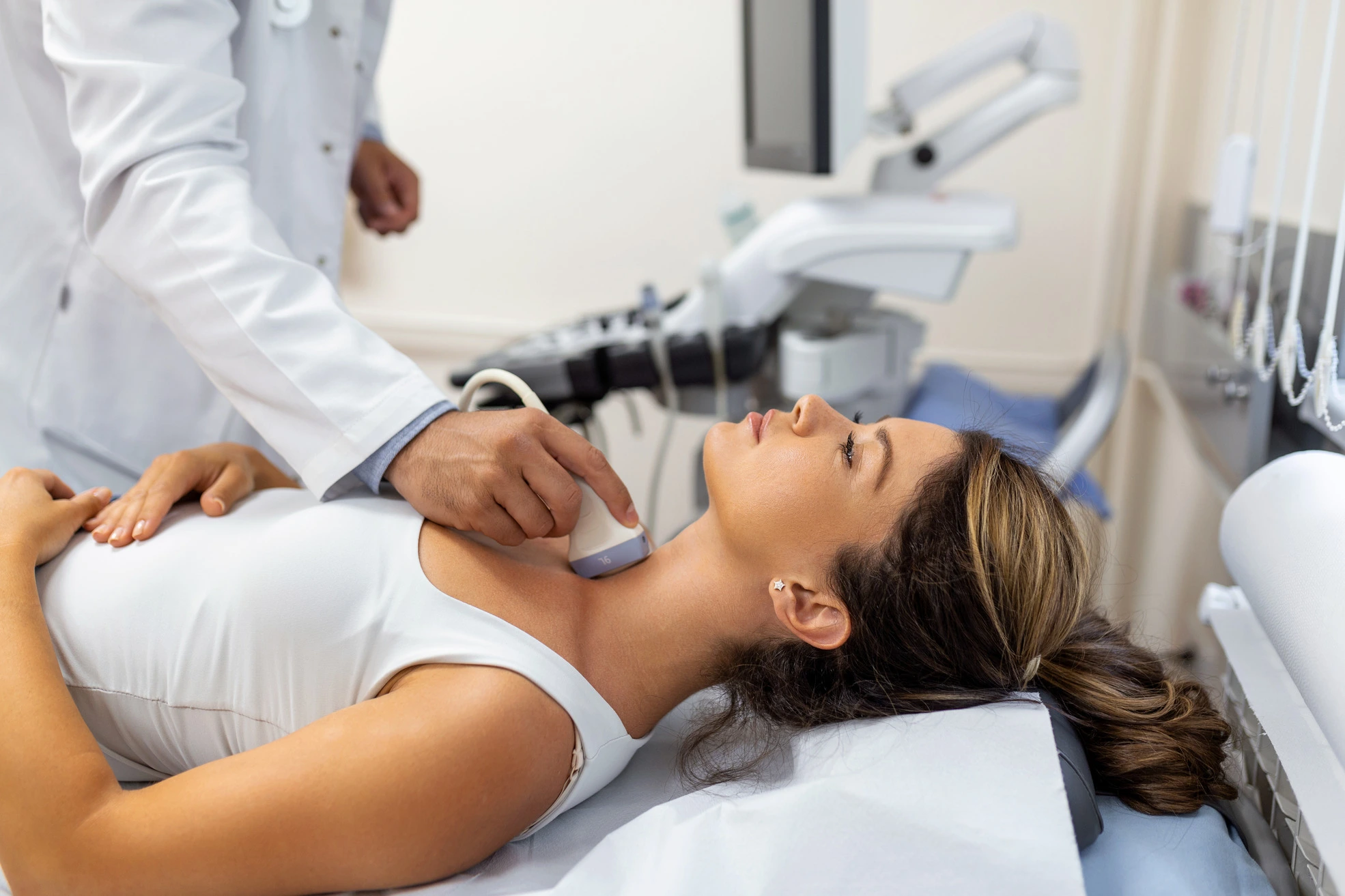
Musculoskeletal USG
We perform ultrasound imaging which uses sound waves to produce pictures of:
Shoulder
Elbow
Wrist
Hip
Knee
Ankle
Foot
Tendo-achilles
Musculoskeletal USG is safe, noninvasive, and does not use ionizing radiation. This procedure requires little to no special preparation.
Mammography
Mammography is a specialized medical technique that uses a low dose X-ray system to look inside the breasts. A Mammogram aids in early detection and diagnosis of breast diseases.
One of the most recent advancements in Mammography is Digital Mammography, also known as Full-Field Digital Mammography (FFDM), uses same systems as a Digital Camera and their efficiency enables better pictures with an even lower radiation dose. These images are transferable by computer and are apt for long-term storage. Patient’s experience during a Digital Mammogram is similar to having a conventional film mammogram.
How should patients prepare for the mammogram?
Before scheduling a mammogram, the American Cancer Society (ACS) and other specialty organizations recommend that patients discuss any new findings or problems in breasts with their doctor. In addition, the patient should inform their physician of any prior surgeries, hormone use, and family or personal history of breast cancer.
It is recommended that patients do not schedule their mammogram for the week before their menstrual period as breasts are usually tender during this time. The best time for a mammogram is one week following the period. The doctor should always inform the technologist if there is any possibility of their patient being pregnant.


The ACS also recommends that:
The patient should not wear deodorant, talcum powder or lotion under their arms or on the breasts on the day of the exam. These can appear on the mammogram as calcium spots.
The patients should describe any breast symptoms or problems to the technologist performing the exam. Patients should obtain their prior mammograms and make them available to the radiologist if they were done at a different location. This is needed for comparison with your current exam and can often be obtained on a CD.
Bone Mineral Density (BMD)
Osteoporosis is a silent disease that can’t be detected until it reaches an advanced symptomatic stage or causes accidental fractures. Hence, regularly monitoring patients for their bone density is the only way a clinician can diagnose osteopenia (low bone mass) or osteoporosis at an early stage.
After this, he can exercise remedial measures. A bone mineral density test is an easy, reliable test that measures the density or thickness of bones, using Dual X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) of the hip and spine, as preferred areas of measurement.
BMD test results are estimated on the basis of:
T-Score
- It’s the patient’s bone mineral density as compared to the peak bone mass in a normal young adult.
- A score of 0 means BMD = normal of a healthy young adult.
- The diagnosis of osteoporosis or low bone mass is based on the T-score.
Z-Score
- It’s the patient’s bone mineral density as compared to the peak bone mass in an age-sex matched adult.
- Z-SCORE is useful for determining whether an underlying disease or condition is causing bone loss.
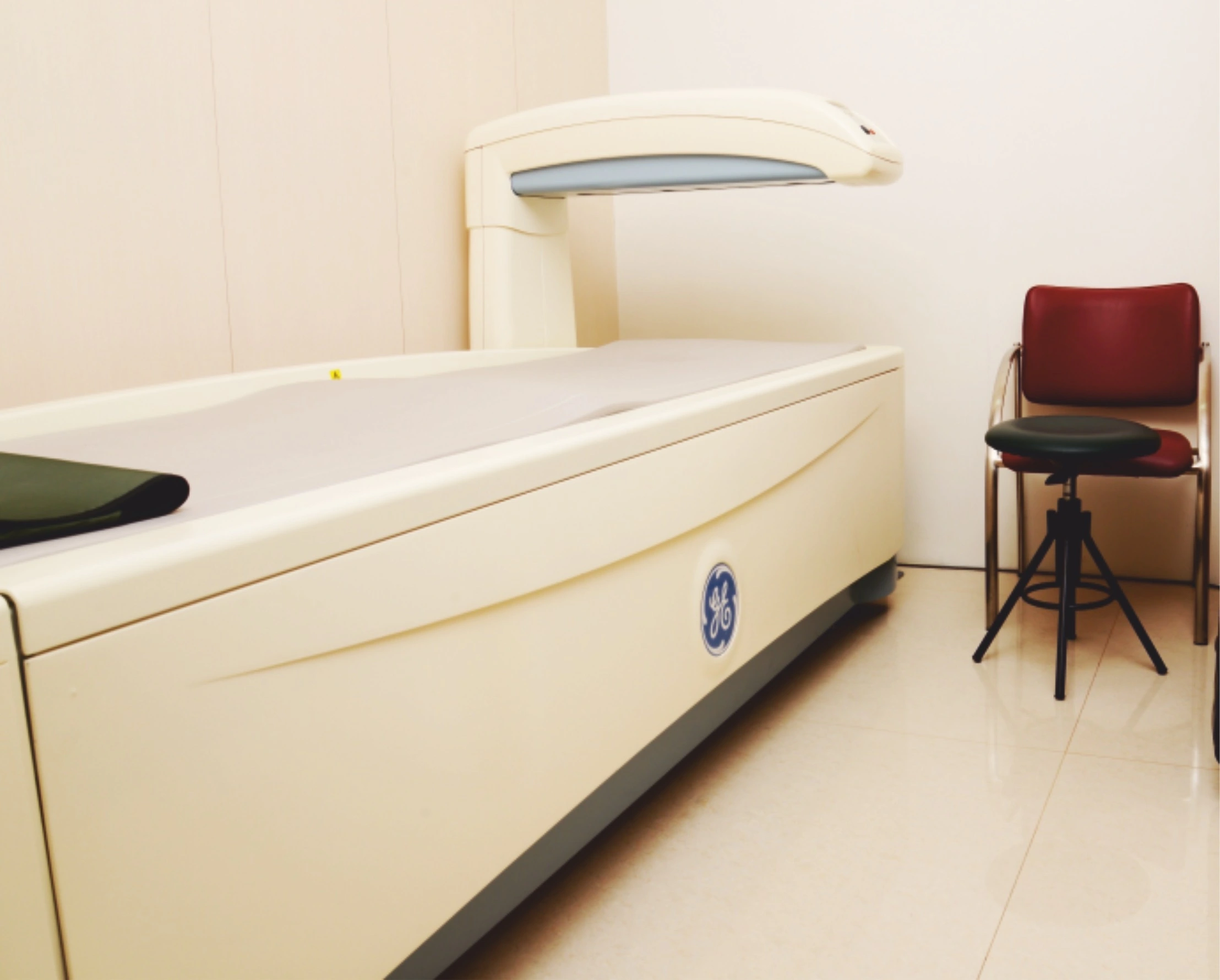

Instructions to Patients for BMD:
- Patients should avoid calcium supplements and multivitamins 24-48 hours prior to the test.
- Clothes with metal buttons or buckles should be avoided.
- Any jewellery or metal which may interfere with the test will have to be removed.
Colour Doppler Ultrasound Test
Suburban Diagnostics offers a range of Colour Doppler test procedures, like:
- Abdominal
- Carotid
- Gravid Uterus
- Renal
- Single Limb Doppler (Arterial and Venous)
- Dual Limb Doppler (Arterial and Venous)
Instructions to Patients for the Colour Doppler Test:
- Generally, no prior preparation is required.
- Patients should carry their prescription and any previous report they may have on the day of the test.
- Any other instructions necessary for the test can be given when the appointment is booked.
Orthopantomography (OPG)
At Suburban Diagnostics, we have a state-of-the-art, specially-assembled OPG machine that rotates around the jawbones, giving us a comprehensive idea about the structure of the jawbones.
No special preparation is required for the test.

